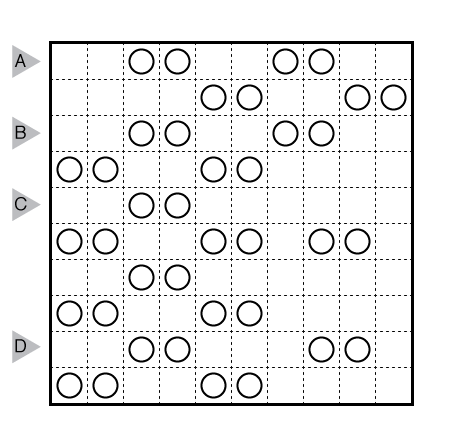
Round Trip by Craig Kasper
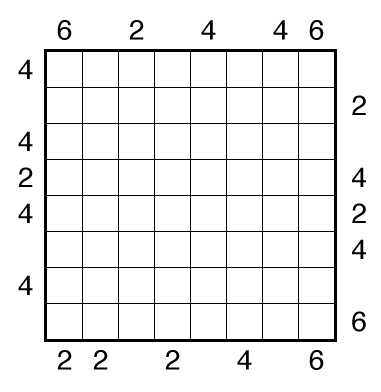
or solve online (using our beta test of Penpa-Edit tools; in default linex mode: left-click+drag draws line, right click marks X on edge)
Theme: Getting Even
Author/Opus: This is the 6th puzzle from guest contributor Craig Kasper.
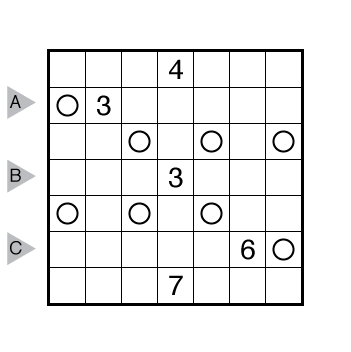
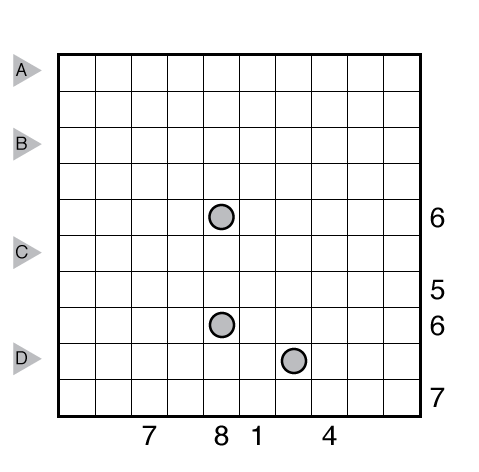
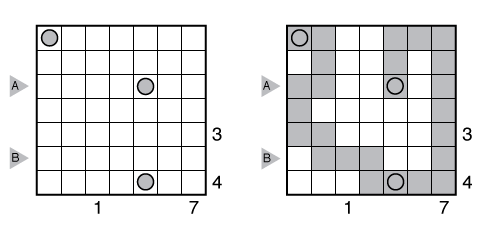
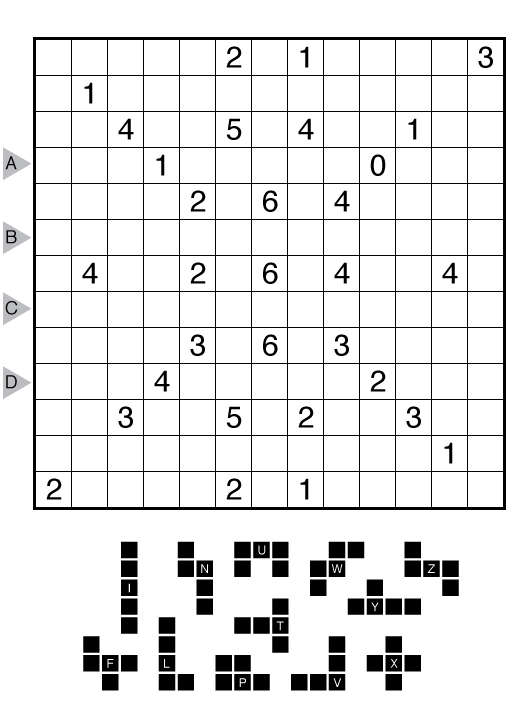
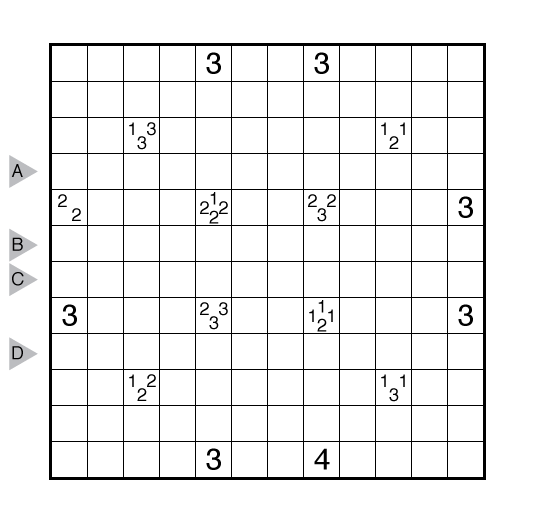
Rules: Draw a single loop in the grid which may cross itself orthogonally, but otherwise does not touch or retrace itself. The clue numbers to the left/right of the rows indicate the number of squares visited by the nearest section of the loop that travels horizontally in the rows. The clue numbers to the top/bottom of the columns indicate the number of squares visited by the nearest section of the loop that travels vertically in the columns.
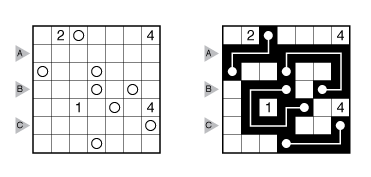
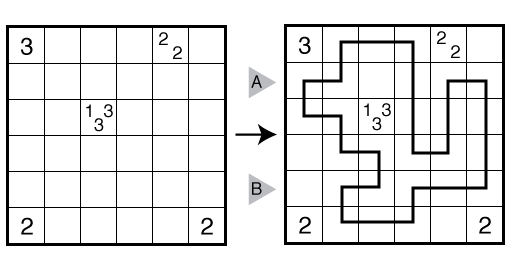
Also, see this example:
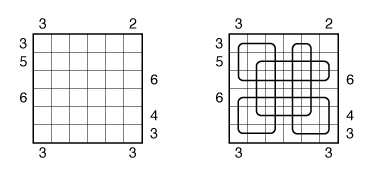
Answer String: Enter the number of empty squares for each row from top to bottom, followed by a comma, and then the number of turns for each row from top to bottom. This example has the key “100000,422224”.
Solution: PDF
Time Standards (highlight to view): Grandmaster = 3:30, Master = 6:00, Expert = 12:00
Note: Follow this link for other Round Trip puzzles. Some more Round Trip puzzles can be found in the book Loop Variety Collection by Ashish Kumar and Murat Can Tonta.